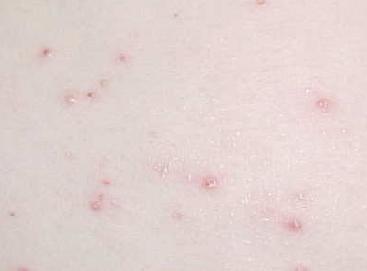
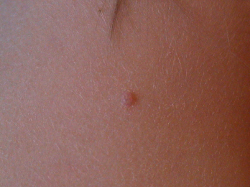
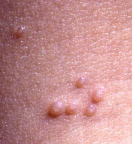
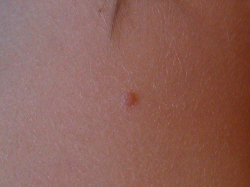
Not every growth in genital area is Molluscum Contagiosum. It is a contagious cutanous tumor that must be diagnosed and treated by an experienced physician (MD) only. Examination, diagnostic biopsy, and treatment is available today at our center.
Upon consultation, we will evaluate and customize your diagnostic treatment plan. Most of our patients get treated in only 1-3 sessions depending on the size, location and number of molluscum. A beneficial cosmetic outcome is always our goal.
Harmful Internet Treatment Remedies / Applications
CDC (Center of Disease Control) warns against internet treatment remedies for Molluscum Contagiosum.
Read here »Should I try to remove the bumps caused by molluscum?
It is not a good idea to try to remove the molluscum growths or to get rid of the fluid inside them yourself.
Be aware that some treatments available through the internet are not effective and may even be harmful!
There are three important reasons not to treat the bumps without seeing a doctor first.
- The treatment may be painful.
- You might spread the bumps to another part of your body or to another person.
- By scratching and scraping the skin you might cause a more serious bacterial infection. If you want to have the growths removed or treated, talk to a health care provider.
Molluscum Contagiosum
Molluscum contagiosum is caused by a poxvirus of the Molluscipox Virus Genus (MCV) that produces a benign papular eruption of multiple umbilicated cutaneous tumors. It is transmitted by direct skin contact and it could be transmitted sexually (STD). It is generally thought to infect humans exclusively, but there are a few isolated reports of Molluscum Contagiosum occurring in pigeons, chickens, chimpanzees, dogs, horses and kangaroos. The infection has a higher incidence rate in those who are immunodeficent.
Molluscum and HIV/AIDS
We know that immunodeficiency is a risk factor for getting molluscum. It is therefore recommended that a patient with a diagnosis of Molluscum Contagiosum also be tested for HIV. For patient peace of mind we are able to perform a HIV test and get the results in a few minutes after a preliminary diagnosis of molluscum is established.
Presentation
Molluscum infection causes small white, pink, or flesh-colored bumps or growths with a dimple or pit in the center. The bumps are usually smooth and firm and can appear anywhere on the body. They may become sore, red, and swollen but are usually painless. When they are picked or stimulated they may cause redness on surrounding tissue. They may increase in size of the patient has an underlying illness such as HIV.
Transmission & Infection
People with this skin disease can cause the bumps to spread to different parts of their body. This is called autoinoculation. Such spread can occur by touching or scratching a bump and then touching another part of the body.
The virus can also be spread from person to person. This can happen if the growths on one person are touched by another person. It can also happen if the virus gets on an object that is touched by other people. Examples of such objects are towels, clothing, and toys. Molluscum can also be spread from one person to another by sexual contact. Anyone who develops bumps in the genital area (on or near the penis, vulva, vagina, or anus) should see a health care provider. Bumps in these areas sometimes mean that molluscum or some other disease was spread through sexual contact.
Treatment
Dr Arani strongly warns against self treatment with non-FDA approved treatment (cream, remedies, oil, home made med, etc.) that may be availble for Molloscum no matter what any websites may claim. "FDA compliant," "FDA registered manufacture" and so on does not mean the product is "FDA approved specifically for molluscum." We have seen numerous cases of patients who were victims of these marketing remedies for molluscum. We strongly advise against these applications. They may encourage viral transmission by stimulation and viral shading.
Molluscum Contagiosum is a sexually transmitted disease and must be treated by an experienced medical doctor only. Once the lesion is treated successfully the virus may be gone and may cease to be contagious.
Can They Come Back Once Removed?
As a general rule if molluscum get treated appropriately and removed then you should have a good chance to be free of them. However, this does not mean that you are immune and you may be re-infected if you are exposed to infected skin or the virus.
Prevention of Viral Tranmission
Keep the area clean! You may cover it with cloth or bandage so others do not touch it and become infected until you are treated.
 Image courtesy Edie Lederman, MD, CDC
Image courtesy Edie Lederman, MD, CDC
Immunity